DTU Electromagnetic Test Centre
The DTU Electromagnetic Test Centre is part of DTU Space at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU, Lyngby Campus, Bldg. 353 and 357) in Lyngby, some 10 km north of Copenhagen.
Finalized in 2024, the DTU Electromagnetic Test Centre (DTU-ETC) is a centre for high-accuracy testing of electromagnetic systems in most of the microwave frequency range from 300 MHz to 300 GHz. DTU-ETC expands significantly the capability of the DTU-ESA Spherical Near-Field Antenna Test facility operated successfully by EMS for decades, and it focuses primarily on testing of antennas over a wide frequency range in several coordinated radio anechoic chambers. DTU-ETC also includes dedicated test facilities and associated know-how for high-accuracy testing of electromagnetic scattering and materials, as well as of high-frequency and high-speed electronics. A brief description of the individual test facilities within the centre is found below. DTU-ETC is used for teaching and research within our research areas, and for collaboration with national and international partners from academia, agencies and industry.
Feel free to contact us if you want to know more about DTU-ETC, and if you are interested in research collaboration and/or have measurement requests within the centre.
DTU-ETC Scattering Test Facility
The facility comprises an anechoic chamber equipped with an NSI-MI provided azimuth positioner, ![]() 2m translation stage, precision motion controller, MI-3000 measurement workstation, and a Keysight 50GHz PNA-L for RCS and scattering measurements and material characterization. The maximum scatterer size and weight are 0.5 m (in diameter) and 25 kg, respectively. The frequency range is 0.3 – 18 GHz.
2m translation stage, precision motion controller, MI-3000 measurement workstation, and a Keysight 50GHz PNA-L for RCS and scattering measurements and material characterization. The maximum scatterer size and weight are 0.5 m (in diameter) and 25 kg, respectively. The frequency range is 0.3 – 18 GHz.
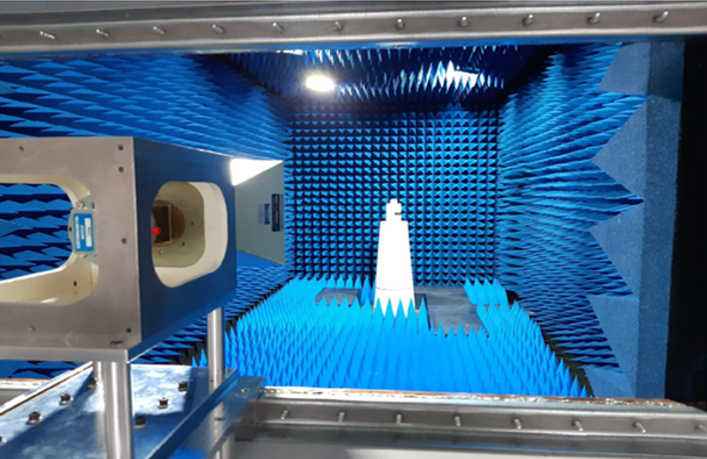
DTU-ETC Planar Near-Field Antenna Test Facility
The facility is based on planar near-field measurement technique and features an anechoic chamber equipped with a planar scanner of area 1.5 m x 0.6 m, antenna positioner, Agilent E8361A VNA, switches and an orthomode transducer. The maximum antenna size and weight are 0.5 m (in diameter) and 25 kg, respectively. The frequency range is 5 – 60 GHz.
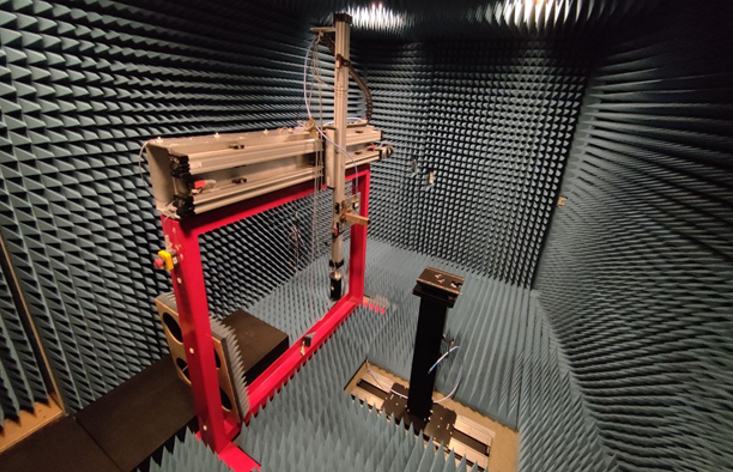
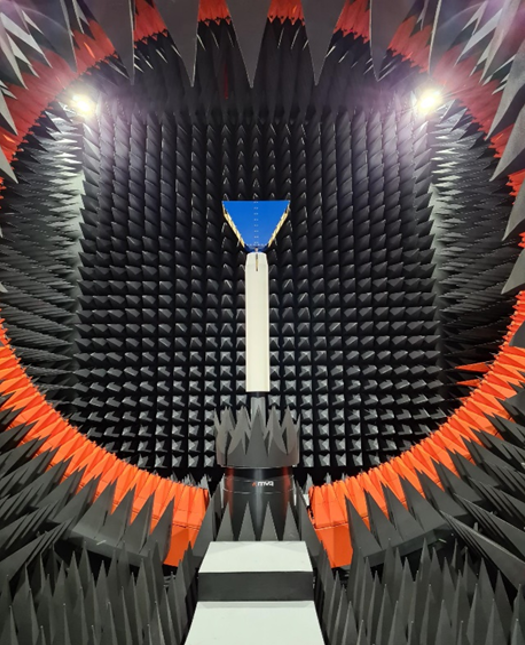
DTU-ETC Fast Antenna Test Facility
The facility is an MVG provided SG Evo spherical near-field antenna test facility. It comprises an anechoic chamber with a circular arch containing an array of 2 x 68 probes and a telescopic mast. The maximum antenna size and weight are 2.5 m (in diameter) and 250 kg, respectively. The frequency range is 0.4 – 18 GHz. The facility is type-approved by Eutelsat, cf., their S.A. requirements, and may thus be used for their antenna characterization campaigns.

DTU-ETC mm-Wave Antenna Test Facility
This is an NSI-MI provided spherical near-field antenna test facility which comprises an anechoic chamber with the NSI-MI SNF-FIX 1.0 system which used a 3-axis swing arm (θ-, ϕ-, and polarization-axes) configuration to position the robot-controlled probe on a spherical surface with the antenna under test remaining stationary. The maximum antenna size and weight are 0.5 m (in diameter) and 10 kg, respectively. The frequency range is 26.5 – 140 GHz.
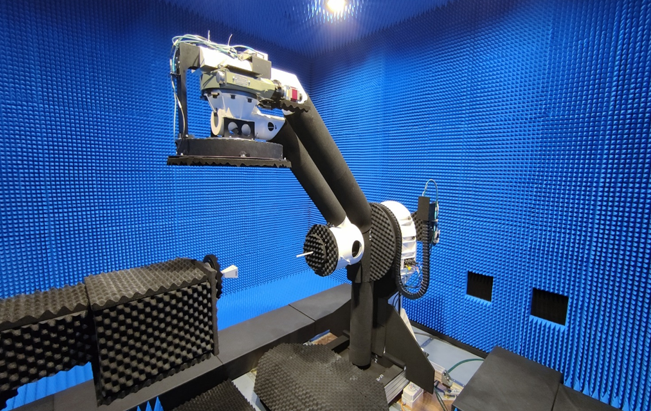
DTU-ETC Multipurpose Antenna Test Facility
This is an NSI-MI provided facility for measurements of, in particular, large earth-observation antennas. It is comprised of a radio anechoic chamber with the NSI-MI SNF-ARM 3.0 swing-arm-based spherical near-field measurement system (radiation pattern determination) and a 5 m travel extrapolation range (gain determination). The maximum antenna size and weight are 3 m (in diameter) and 2000 kg, respectively. The frequency range is 0.3 – 110 GHz. Finalization expected in October 2024.
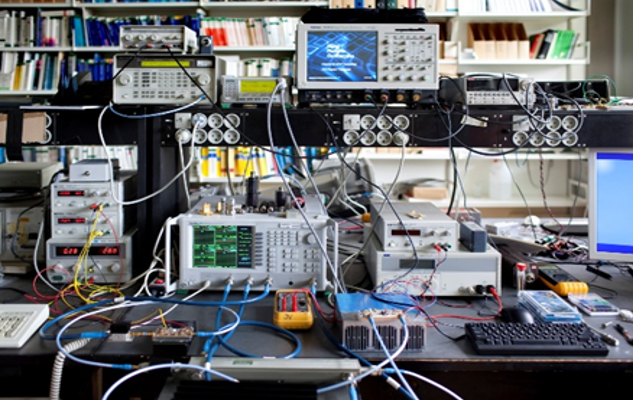
DTU-ETC mm-Wave Component and Circuit Test Facility
Present capability includes on-wafer measurements and accurate characterization of integrated circuits up to 170 GHz. The facility features a shielded room with network analysis up to 170 GHz, spectrum analysis up to 26.5 GHz, probes for on-wafer measurements from DC to 170 GHz, signal generation, direct (up to 40 GHz) and multiplied (up to 170 GHz), and power/noise measurements up to 18 GHz. Significant expansion of these capabilities is planned in the near future.